This article is more than 1 year old
Astronomers find first neutron star in Andromeda galaxy
Lighthouse in space spotted in years of records
Neutron stars have been found in our own galaxy for decades, but now scientists have spotted the first in our galactic neighbor Andromeda.
A neutron star is the remnant of a once-bright star that has since gone supernova and spins rapidly. If an extremely dense remnant encounters another star it sucks off its material, resulting in blasts of radiation that sweep out like a lighthouse.
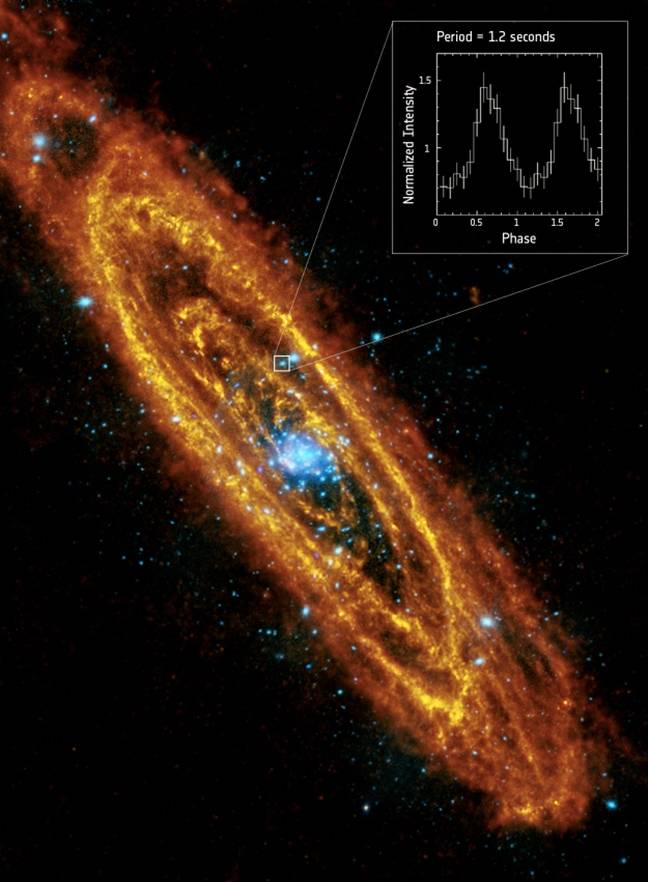
"We were expecting to detect periodic signals among the brightest X-ray objects in Andromeda, in line with what we already found during the 1960s and 1970s in our own Galaxy," said Gian Luca Israel, from INAF-Osservatorio Astronomica di Roma, Italy.
"But persistent, bright X-ray pulsars like this are still somewhat peculiar, so it was not completely a sure thing we would find one in Andromeda. We looked through archival data of Andromeda spanning 2000-2013, but it wasn't until 2015 that we were finally able to identify this object in the galaxy's outer spiral in just two of the 35 measurements."
The finding is an important confirmation that such stars are relatively common, but the Andromeda example is unusual in its movements. The star spins once every 1.2 seconds and the star it feasts on orbits it every 1.3 days.
A bright spark in a far-off galaxy
"It could be what we call a 'peculiar low-mass X-ray binary pulsar' – in which the companion star is less massive than our Sun – or alternatively an intermediate-mass binary system, with a companion of about two solar masses," says Paolo Esposito of INAF-Istituto di Astrofisica Spaziale e Fisica Cosmica in Italy.
"We need to acquire more observations of the pulsar and its companion to help determine which scenario is more likely."
Andromeda is 2.5 million light years away, so detailed observations of the new star are impossible – for the moment. We'll be able to get a lot closer look in about four billion years' time, at which point the Andromeda galaxy will collide with our Milky Way and merge into a new super-galaxy.
More findings on the new star can be found in the Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. ®
